Unit 8
Microsoft Windows Security Configuration
Learning Objectives
Learn how to implement proper file-level permissions on Windows systems
Purpose, use, and types
Permission inheritance and parent/child relationships
Customization
Understand how backups function and best-practice backup strategies
Availability and integrity
Major backup techniques and types
Configuration
Understand how audit logging and system monitoring are performed and configured
Audit logging purpose and configuration
Performance monitoring purpose and configuration
Section 1
Windows File Protections
The CIA Triad (Review)
3 Goals of information security:
Maintain information confidentiality
Making sure only approved users have
access to data
Maintain information
integrity
Data Integrity: assurance that information has not been tampered with or corrupted between the source and the end user
Source Integrity:assurance that the sender of the information is who it is supposed to be
Maintain information availability
- Ensuring data is accessible by approved users when needed
File Permissions
Important tool for ensuring data integrity and confidentiality
More customizable than the blanket set of permissions given to users by adding them to either the Users or Administrators group
Use to restrict access or editing rights to specific data on shared resources
Can be customized by individual user or by user group
File Permissions
Restrict access or editing rights to data on shared resources
Types of permissions:
Full Control
Modify
Read & Execute
List Folder Contents
Write
Read
Types of File Permissions
Full Control
Administrator level access
Users can make every possible change to a selected file or the contents of a selected folder
Modify
Allows users to change a file’s content, but not its ownership
Users cannot delete the file
Read & Execute
- Allows users to open and run programs
List Folder Contents
- Allows users to view the names of files stored in the selected folder
Write
- Allows users to make changes to a file and overwrite existing content
Read
- Allows users to view the attributes of a file or folder, but not edit it
Inheritable Permissions
By default, objects within a folder (known as child objects) inherit permission settings from their containing folder (known as the parent object)
You can turn off inheritable permissions and customize who gets
what kind of access to certain folders, subfolders, or documents
Depending on how many users need access to a sensitive file or folder and how many of the files in a folder need to be restricted, there are several ways to apply permissions
- Example: If you want certain users or groups to be denied access to all but a few files within a folder, it is quickest to apply a restrictive permission setting to the parent object (folder). Once you have denied those users’ access to all of the files in the folder, you can go to the individual files you do want them to have access to and override the permissions those files inherited from the parent folder.
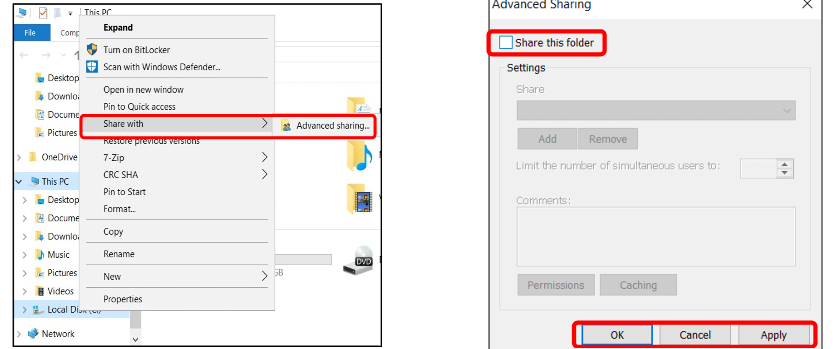
Sharing Drives
You can share an entire network’s files by sharing its drives
Generally not a good idea – Anyone could see or modify your files
To turn off Sharing Drives: Open File Explorer→ Click This PC→ Right Click the Local Disk Drive → Share with → Advanced Sharing → Uncheck Share this folder → Click OK
Creating Backups
Control Panel System and Security Backup and restore
System image: Contains files, programs, system files, and settings
Create a System repair disc: Contains necessary system files
Section 2
Windows Auditing and Monitoring
Event Viewer
Displays logs of events occurring on the Windows operating system
Control Panel → System and Security → Administrative Tools → Event Viewer
OR Search → Event Viewer
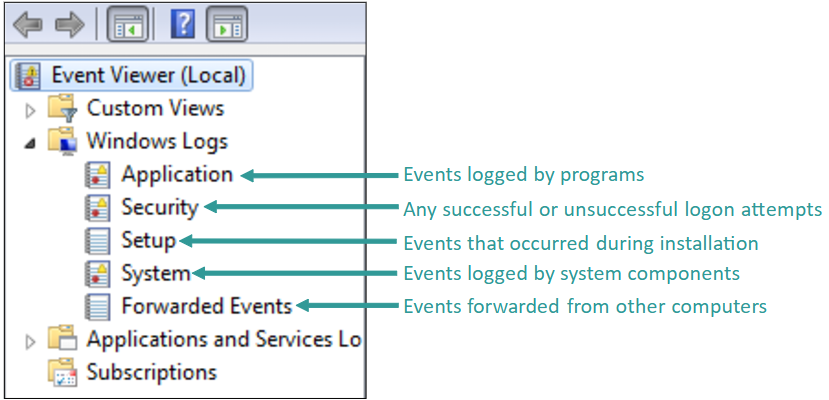
Windows Logs
Security logs can be a useful last defense against attacks and a tool for forensics investigations into the source of a past attack or unauthorized entry
Customize what security logs are kept by setting Audit Policies
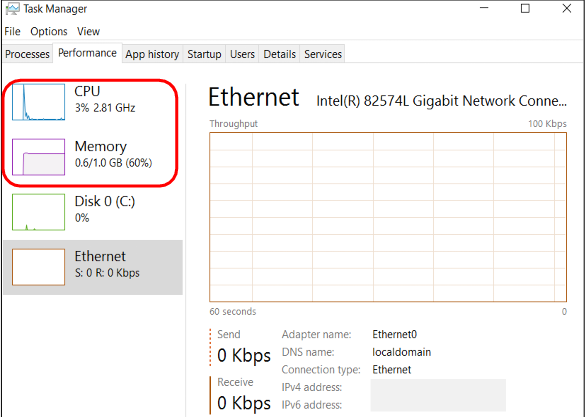
Task Manager
Shows programs, services, and processes currently running
Shows network activity and resource utilization
Search → Task Manager
Task Manager: Performance
CPU: Monitors current and past resource use
CPU usage by core
Multi-core Processors
Task Manager: Performance (cont.)
Memory Usage
Task Manager: Performance Tab
Performance problems can arise from a broken router, switch, or cable, or from the
computer itself
To see resource utilization details: Click Open Resource Monitor